Description
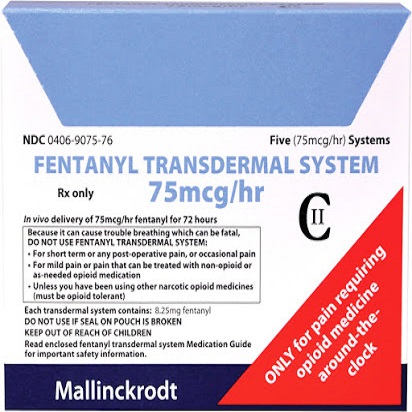
Buy Fentanyl Transdermal System 75mcg/h Online
Buy Fentanyl Transdermal System 75mcg/h Online, Fentanyl transdermal system contains a high concentration of a potent Schedule II opioid agonist, fentanyl. Schedule II opioid substances which include fentanyl, hydromorphone, methadone, morphine, oxycodone, and oxymorphone have the highest potential for abuse and associated risk of fatal overdose due to respiratory depression. Fentanyl can be abused and is subject to criminal diversion. The high content of fentanyl in the patches (fentanyl transdermal system) may be a particular target for abuse and diversion.
Fentanyl transdermal system is indicated for management of persistent , moderate to severe chronic pain that:
- requires continuous, around-the-clock opioid administration for an extended period of time, and
- cannot be managed by other means such as non-steroidal analgesics, opioid combination products, or immediate-release opioids
Fentanyl transdermal system should ONLY be used in patients who are already receiving opioid therapy, who have demonstrated opioid tolerance, and who require a total daily dose at least equivalent to fentanyl transdermal system 25 mcg/hr. Patients who are considered opioid-tolerant are those who have been taking, for a week or longer, at least 60 mg of morphine daily, or at least 30 mg of oral oxycodone daily, or at least 8 mg of oral hydromorphone daily or an equianalgesic dose of another opioid.
Because serious or life-threatening hypoventilation could occur, fentanyl transdermal system is contraindicated:
- in patients who are not opioid-tolerant
- in the management of acute pain or in patients who require opioid analgesia for a short period of time
- in the management of post-operative pain, including use after out-patient or day surgeries (e.g., tonsillectomies)
- in the management of mild pain
- in the management of intermittent pain (e.g., use on an as needed basis [prn])
(see CONTRAINDICATIONS for further information).
Since the peak fentanyl concentrations generally occur between 24 and 72 hours of treatment, prescribers should be aware that serious or life-threatening hypoventilation may occur, even in opioid-tolerant patients, during the initial application period.
The concomitant use of fentanyl transdermal system with all cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors (such as ritonavir, ketoconazole, itraconazole, troleandomycin, clarithromycin, nelfinavir, nefazodone, amiodarone, amprenavir, aprepitant, diltiazem, erythromycin, fluconazole, fosamprenavir, grapefruit juice, and verapamil) may result in an increase in fentanyl plasma concentrations, which could increase or prolong adverse drug effects and may cause potentially fatal respiratory depression. Patients receiving fentanyl transdermal system and any CYP3A4 inhibitor should be carefully monitored for an extended period of time and dosage adjustments should be made if warranted (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Drug Interactions; WARNINGS; PRECAUTIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION for further information).
The safety of fentanyl transdermal system has not been established in children under 2 years of age. Fentanyl transdermal system should be administered to children only if they are opioid-tolerant and 2 years of age or older (see PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use).
Fentanyl transdermal system is ONLY for use in patients who are already tolerant to opioid therapy of comparable potency. Use in non-opioid tolerant patients may lead to fatal respiratory depression. Overestimating the fentanyl transdermal system dose when converting patients from another opioid medication can result in fatal overdose with the first dose (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Initial Fentanyl Transdermal System Dose Selection). Due to the mean half-life of approximately 17 hours, patients who are thought to have had a serious adverse event, including overdose, will require monitoring and treatment for at least 24 hours.
Fentanyl transdermal system can be abused in a manner similar to other opioid agonists, legal or illicit. This risk should be considered when administering, prescribing, or dispensing fentanyl transdermal system in situations where the healthcare professional is concerned about increased risk of misuse, abuse or diversion.
Persons at increased risk for opioid abuse include those with a personal or family history of substance abuse (including drug or alcohol abuse or addiction) or mental illness (e.g., major depression). Patients should be assessed for their clinical risks for opioid abuse or addiction prior to being prescribed opioids. All patients receiving opioids should be routinely monitored for signs of misuse, abuse and addiction. Patients at increased risk of opioid abuse may still be appropriately treated with modified-release opioid formulations; however, these patients will require intensive monitoring for signs of misuse, abuse, or addiction.
Fentanyl transdermal systems are intended for transdermal use (on intact skin) only. Do not use a fentanyl transdermal system if the pouch seal is broken or the patch is cut, damaged, or changed in any way.
Avoid exposing the fentanyl transdermal system application site and surrounding area to direct external heat sources, such as heating pads or electric blankets, heat or tanning lamps, saunas, hot tubs, and heated water beds, while wearing the system. Avoid taking hot baths or sunbathing. There is a potential for temperature-dependent increases in fentanyl released from the system resulting in possible overdose and death. Patients wearing fentanyl transdermal systems who develop fever or increased core body temperature due to strenuous exertion should be monitored for opioid side effects and the fentanyl transdermal system dose should be adjusted if necessary. Buy Fentanyl Transdermal System 75mcg/h Online